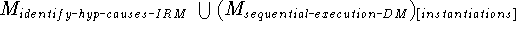A. Constituents
B. Compatibility conditions
1.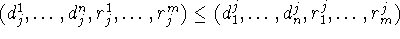
2. For every
and partially instantiated input axiom
in which
arguments intervene it holds that either
a., if the input axiom is of the form
; or
b., if the input axiom is of the form
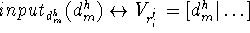
C. Extended KL-structure

instantiations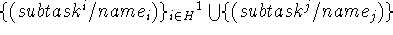
import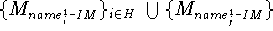
input axioms and program of
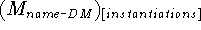
Example We describe one step in the construction of the
instantiated decomposition method mechanical advise from a
reusable KL-component (the generic decomposition method
sequential execution, defined in section 2.1) and a simpler
KL-structure (the instantiated resolution method identify
hypothetical causes, defined above). In particular, we show how the
instantiated method identify hypothetical causes is assigned to
one of the uninstantiated subtasks, ![]() , of the instantiated
decomposition method mechanical advise.
, of the instantiated
decomposition method mechanical advise.
As we have shown already, the formal descriptions of KL-components and KL-structures can be formally manipulated by mathematical operations. Our composition rules constitute a particular type of such operations, which allow connecting, disconnecting and substituting KL-components and KL-structures within other KL-structures. There are also other types of operations, which can be used to generalize or specialize the formal descriptions of KL-components and KL-structures. We show below how a specialization operation can be applied to the generic decomposition method sequential execution (which handles an arbitrary number m of subtasks, see its definition in section 2.1), in order to make it fit into the binary task decomposition and arguments of the instantiated resolution method at hand.
First, the definition of sequential execution is specialized by
setting the values of the parameters ![]() . We set
. We set ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The formal
description of the resulting specialized sequential execution
decomposition method is as follows.
. The formal
description of the resulting specialized sequential execution
decomposition method is as follows.

predicates sequentialexecution
variables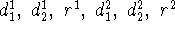
metavariables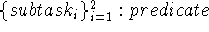
axioms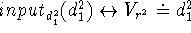
program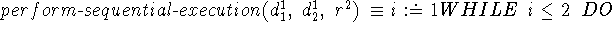
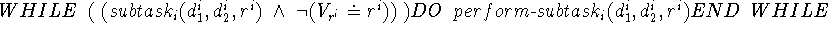
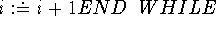
Then, the instantiated method identify hypothetical causes is
assigned to the uninstantiated subtask, ![]() , of the
specialized version of the decomposition method sequential
execution, through the application of composition rule II.
, of the
specialized version of the decomposition method sequential
execution, through the application of composition rule II.
A. Constituents
B. Compatibility Conditions
1.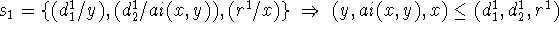
2. There are no instantiated input axioms yet.
C. Extended KL-structure

instantiations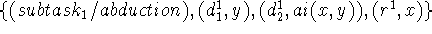
import