
Next: Corporate Memories as
Up: Corporate Memories as Distributed
Previous: Distributed Processing
vs
A Case-based Reasoning (CBR) system uses lazy "generalization" from
past similar cases to the present task. Past similar cases are
retrieved through similarity estimates between the current problem 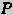 and the precedent cases
and the precedent cases
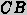 that the system has
access to.
The
crucial assumption in a CBR system is that the more similar the
current problem
that the system has
access to.
The
crucial assumption in a CBR system is that the more similar the
current problem 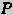 is to
a
precedent
is to
a
precedent 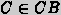 , the more
similar
the solution of
, the more
similar
the solution of 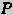 is to
the
solution of
is to
the
solution of 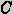 . In
recent times,
CBR techniques have enjoyed an immense popularity among researchers
and practitioners of AI, building intelligent tools for a number of
applications[Aamodt &Plaza1994].
Techniques for distributed case-based
reasoning are being developed with the aim of leveraging the insights
gained from building and using such applications but at the same time
coping with the distributed nature of the knowledge available in many
applications. Viewing Corporate Memories as Distributed Case Libraries
(or Distributed Case Bases) provides us with ways to exploit these
techniques to develop semantically rich and flexible tools for
knowledge management in distributed environments.
. In
recent times,
CBR techniques have enjoyed an immense popularity among researchers
and practitioners of AI, building intelligent tools for a number of
applications[Aamodt &Plaza1994].
Techniques for distributed case-based
reasoning are being developed with the aim of leveraging the insights
gained from building and using such applications but at the same time
coping with the distributed nature of the knowledge available in many
applications. Viewing Corporate Memories as Distributed Case Libraries
(or Distributed Case Bases) provides us with ways to exploit these
techniques to develop semantically rich and flexible tools for
knowledge management in distributed environments.
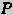 and the precedent cases
and the precedent cases
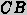 that the system has
access to.
The
crucial assumption in a CBR system is that the more similar the
current problem
that the system has
access to.
The
crucial assumption in a CBR system is that the more similar the
current problem 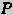 is to
a
precedent
is to
a
precedent 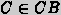 , the more
similar
the solution of
, the more
similar
the solution of 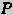 is to
the
solution of
is to
the
solution of 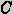 . In
recent times,
CBR techniques have enjoyed an immense popularity among researchers
and practitioners of AI, building intelligent tools for a number of
applications[Aamodt &Plaza1994].
Techniques for distributed case-based
reasoning are being developed with the aim of leveraging the insights
gained from building and using such applications but at the same time
coping with the distributed nature of the knowledge available in many
applications. Viewing Corporate Memories as Distributed Case Libraries
(or Distributed Case Bases) provides us with ways to exploit these
techniques to develop semantically rich and flexible tools for
knowledge management in distributed environments.
. In
recent times,
CBR techniques have enjoyed an immense popularity among researchers
and practitioners of AI, building intelligent tools for a number of
applications[Aamodt &Plaza1994].
Techniques for distributed case-based
reasoning are being developed with the aim of leveraging the insights
gained from building and using such applications but at the same time
coping with the distributed nature of the knowledge available in many
applications. Viewing Corporate Memories as Distributed Case Libraries
(or Distributed Case Bases) provides us with ways to exploit these
techniques to develop semantically rich and flexible tools for
knowledge management in distributed environments.