
Next: Multi-agent
Protein Purification
Up: Federated Peer
Learning
Previous: Agent
Communication with
Cooperation among CBR agents involves exploiting the set of precedents
in the collective memories of all the agents for use in
similarity-based reasoning. There are two general ways to do so:
DistCBR and ColCBR. Intuitively, both DistCBR and ColCBR are based on
solving a problem by reusing the knowledge learned by other CBR
agents. Given an agent (the originator) trying to solve a
problem, the difference between both modes is in the similarity-based
reasoning method used: that of the originator or that of the CBR agent
that is helping the originator.
From the standpoint of implementing these cooperation modes, we can say
that DistCBR is supported by the remote evaluation capability and ColCBR is
supported by remote programming (or mobile code) capability of Plural
Noos.


Next: Multi-agent
Protein Purification
Up: Federated Peer
Learning
Previous: Agent
Communication with
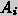 transmitting the problem and the task
to be achieved to another agent
transmitting the problem and the task
to be achieved to another agent 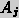 . Agent
. Agent 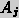 uses its own CBR method
and its case base
uses its own CBR method
and its case base 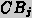 to
achieve the task and send the results back
to agent
to
achieve the task and send the results back
to agent 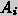 . In case of
failure, a failure token is sent back and
. In case of
failure, a failure token is sent back and
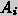 can iterate the
cooperation tasks with the next agent of its preference.
can iterate the
cooperation tasks with the next agent of its preference.
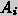 transmitting the method that
is to be used to solve a task, in addition to the problem and the task
to be achieved, to another agent
transmitting the method that
is to be used to solve a task, in addition to the problem and the task
to be achieved, to another agent 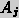 . Agent
. Agent 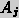 will use its case
base
will use its case
base 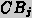 and the method
sent by
and the method
sent by 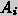 to achieve the
task and send
back the results. In other words, the originator is using the memory
of the other agents as an extension of its own - as a collective
memory - by means of being able to impose on other agents the use of
its own CBR methods. In case of failure, a failure token is sent back
and
to achieve the
task and send
back the results. In other words, the originator is using the memory
of the other agents as an extension of its own - as a collective
memory - by means of being able to impose on other agents the use of
its own CBR methods. In case of failure, a failure token is sent back
and 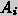 can iterate the
cooperation tasks with the next agent of its
preference.
can iterate the
cooperation tasks with the next agent of its
preference.