- ...jsierra@dia.fi.upm.es
- Current address: Stanford University,
Gates Computer Science Building
2A, Room 206,
Stanford, CA 94305-9020,
phone: (415)723-4910,
fax: (415)725-7411,
email: jsierra@cs.stanford.edu
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...another
- The expression (L,A) denotes a
theory with language -non-logical symbols- L and axioms A.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...functions
- Note that this example
uses only propositional logic language. The argument of all functions and
predicates, (e.g., the particular car with failure) is omitted because
it carries no extra information.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...ask
67#1
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...abduction
- In fact,
it is connected to the instantiated resolution method
identify-hyp-causes, through a second application of rule I.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...axiom
- A decomposition method input axiom is a formula
of the form
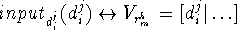 , which describes how the inputs of some subtasks are obtained
from the values of state variables containing the output values of
other subtasks. There are other types of input axioms as well (see
the definition of decomposition method in section 2.1), but we
shall not consider them here.
, which describes how the inputs of some subtasks are obtained
from the values of state variables containing the output values of
other subtasks. There are other types of input axioms as well (see
the definition of decomposition method in section 2.1), but we
shall not consider them here.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...of
-
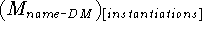 denotes the result of
applying the substitutions in [instantiations] to the axioms and program
parts of
denotes the result of
applying the substitutions in [instantiations] to the axioms and program
parts of  .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.