

Next: About this document
Up: Software Agents Based on
Previous: Acknowledgments
References
- Aben 95
- Aben, M. (1995). Formal Methods in Knowledge
Engineering. Ph. D. thesis, Universiteit van Amsterdam.
- Brazier, Keplicz, Jennings and Treur 95
-
Brazier, F., Keplicz, B.D., Jennings, N.R., and Treur, J. (1995)
Formal Specification of Multi-Agent Systems: A Real-World Case.
Proceedings of the First International Conference on Multi-Agent
Systems.
- Chandrasekaran 86
- Chandrasekaran, B. (1986).
Generic tasks in knowledge-based reasoning: High level building blocks
for expert system design. IEEE Expert, 1(3):23-30.
- Clancey 83
- Clancey, W.J. (1983). The epistemology
of rule-based expert systems - a framework for explanation.
Artificial Intelligence, 20:215-251.
- Cuena 93
- Cuena, J. (1993). Contributions
to a Knowledge Oriented View of Software de Design. In
Knowledge Oriented Software Design. J. Cuena, (Ed.)
Elsevier.
- Fensel and van Harmelen 94
- Fensel D., and van Harmelen F.
(1994). A comparison of languages which operationalize and formalize
KADS models of expertise. The Knowledge Engineering Review,
Vol 9:2, 105-146.
- Genesereth and Ketchpel 94
- Genesereth M.R., and
Ketchpel S.P. Software Agents. Communications of the ACM, Vol 37,
nr 7.
- Gruber and Olsen 94
- Gruber T., and Olsen G.R.
(1994). An Ontology for Engineering Mathematics. Technical report
KSL-94-18, Knowledge Systems Laboratory, Stanford University.
- Harel 84
- Harel, D. (1984). Dynamic logic.
Gabbay, D, and F. Guenthner (Eds.), Handbook of Philosophical
Logic, Vol. II: extensions of Classical Logic, pp 497-604. Dordrecht,
the Netherlands: Reidel Publishing Company.
- van Harmelen 91
- van Harmelen, F. (1991).
Meta-level Inference Systems. Research Notes in AI. London, San
Mateo California, Pitman, Morgan Kaufmann.
- van Harmelen and Balder 92
- Van Harmelen F., and Balder
J.R. (1992).
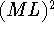 : a formal language for KADS models of
expertise. Knowledge Acquisition, Vol 4, nr 1, March 1992, pp.
127-161. Special issue: The KADS approach to knowledge
engineering.
: a formal language for KADS models of
expertise. Knowledge Acquisition, Vol 4, nr 1, March 1992, pp.
127-161. Special issue: The KADS approach to knowledge
engineering.
- Helm, Holland and Gangopadhyay 90
-
Helm, R., Holland, I.M., and Gangopadhyay, D. (1990) Contracts:
Specifying Behavioral Compositions in Object-Oriented Systems. In
OOPSLA'90 Proceedings.
- Newell 82
- Newell, A. (1982). The knowledge level.
Artificial Intelligence, 18:87-127.
- Sierra 96
- Sierra, J. (1996). Software Agents
Require Formal KL-Models. Ph.D. thesis. Free University of Brussels.
- Steels and Mc Dermott 92
- Steels, L., and Mc Dermott,
J. (Eds.). (1992). Knowledge level expert systems research in action.
Academic Press. London.
- Steels 90
- Steels, L. (1990). Components of
Expertise. AI Magazine, Vol 11(2):29-49.
- Steels 92a
- Steels L. (1992). Reusability
and Configuration of Applications by Non-programmers. Proc.
Artificial Intelligence from the Information Processing
Perspective (Workshop AIFIPP-92), Madrid.
- Steels 92b
- Steels, L. (1992). The componential
framework and its role in reusability. In: David, J.M., and
J.P. Krivine. Second Generation Expert Systems. Berlin, Springer
Verlag.
- Steels 94
- Steels, L. (1994). Beyond Objects,
AI-MEMO 94-4. Also in Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on
Object Oriented Programming.
- Tarsky 36
- Tarsky, A. (1956). Der Wahrheitsbegriff
in den formalisierten Sprachen. Studia Philosophica, 1,
261-405, 1936. English translation in A. Tarsky. Logic,
Semantics, Metamathematics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Tokoro 93
- Tokoro, M. (1993). The Society of Objects.
Invited talk at OOPSLA'93. Addendum to OOPSLA'93 Proceedings.
- Treur and Wetter 93
- Treur J. and Wetter Th. (Eds.).
(1993). Formal Specification of Complex Reasoning Systems, Ellis
Horwood.
- van de Velde 91
- van de Velde, W. (1991).
Incremental Learning of Optimal Decision Trees. Technical report
TR-1-91, CEAB, Barcelona.
- van de Velde 93
- van de Velde, W. (1993).
Issues in knowledge level modelling. In Second Generation in
Expert Systems, p. 211-231. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Walther 87
- Walther, C. (1987). A Many-Sorted
Calculus Based on Resolution and Paramodulation. Research Notes
in Artificial Intelligence. London: Pitman.
- Wielinga, Schreiber, and Breuker 92
- Wielinga B.J.,
Schreiber A.T., and Breuker J.A. (1992). KADS: A modelling
approach to knowledge engineering. Knowledge Acquisition, vol. 4(1),
pp. 127-161. Special issue The KADS approach to knowledge
engineering.
jsierra@cs.stanford.edu